New fiber bamboo fiber
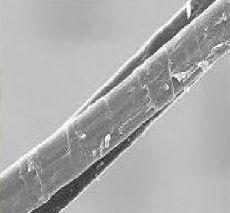
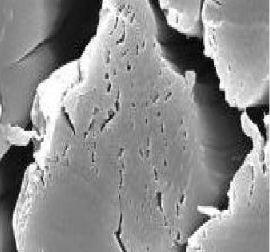
Bamboo fiber is a cellulose fiber extracted from naturally grown bamboo, followed by cotton, hemp, wool, and silk. Divided into natural bamboo fiber and chemical bamboo fiber. Bamboo fiber has good gas permeability, instant water absorption, strong wear resistance and good dyeing properties, and at the same time has natural antibacterial, antibacterial, antimony, deodorant and anti-ultraviolet functions. Bamboo fiber is a natural environmentally friendly green fiber in the true sense. Bamboo fiber introduction Natural bamboo fiber: Natural bamboo fiber is mainly bamboo fiber, which is a natural bamboo fiber obtained by a combination of physical and chemical methods. Chemical bamboo fiber: Chemical bamboo fiber is divided into bamboo pulp fiber and bamboo charcoal fiber. Bamboo pulp fiber: It is a kind of pulp made of bamboo, then the pulp is made into pulp and then wet-spun into fiber. The manufacturing process is basically similar to that of glue. Bamboo charcoal fiber: It is a fiber product which is selected from nanometer bamboo charcoal powder and added into viscose spinning solution through special process and then weaved by similar conventional spinning process. Chemical composition and morphological structure of bamboo fiber chemical components The chemical constituents of bamboo fiber are mainly cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. It also contains a small amount of other substances such as ash. In China, the main producing areas of bamboo are Gansu, Sichuan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian and Hunan. The chemical composition of bamboo fiber is also different due to the different origin. Cellulose is the most important component of bamboo fiber, but the content of cellulose in bamboo fiber is obviously lower than that of cotton and hemp fiber. Generally, the cellulose content of domestic bamboo is about 44%~53%; hemicellulose is complex glycan It is an amorphous substance, so the degree of polymerization is low, moisture absorption is easy to swell, and it is a "binder" and a "filler" between fibers and microfibers, wherein the content of polypentose is about 17%~26 %; lignin is an aromatic polymer compound formed by a phenylpropane structural unit through an ether bond or a carbon-carbon bond, and is located between the intercellular layer and the fine fiber, and its content is generally 23% to 34%, which is produced. The main factor of bamboo fiber color; the main component of pectin is a derivative of pectic acid, which is widely found in plants in nature. Ash is composed of various inorganic salts, and the main constituent of ash in bamboo fibers is SiO2. Morphology The single bamboo fiber is slender, with pointed ends and a spindle shape. The inner wall of the fiber is smooth, the cell wall is thick, and the cell cavity is small. The longitudinal fiber surface of the bamboo fiber is smooth and uniform, and there are a plurality of shallow grooves. The elliptical cross section is covered with an elliptical gap, which is arranged in a plum blossom shape, is hollow, and has a very strong capillary effect. The edges are irregularly zigzag. Bamboo fibrils: elliptical or rounded, with a middle cavity, cracks at the edges of the section, and many micropores; longitudinal sections. Bamboo fiber cross section Bamboo fiber longitudinal section Bamboo pulp fiber: The cross-section zigzag has many micropores; the longitudinal direction has grooves. Bamboo pulp fiber surface Bamboo pulp fiber cross section Bamboo fiber processing method Native method for producing bamboo fiber After the bamboo is repeatedly rolled by physical and mechanical methods, the degumming process is used to partially degumming, and the partially degummed bamboo fiber residual glue connects the bamboo fibers one by one to form the desired bamboo fiber. This kind of fiber is not a single fiber, but a bundle of fibers. Its fineness is generally 20~50tex, and the hard wire and the wire are many, and the water content is 13%. Since the glue is not depleted, its color is yellowish. In the dry state, the dust is large, and the strength is very low when wet. Therefore, drying and oiling must be performed before processing to increase the softness and strength of the fiber. Regeneration method for producing bamboo fiber After slicing and air drying the bamboo, the bamboo pieces are chemically prepared into pulps that meet the requirements for fiber production, and are dissolved and spun. The fiber eliminates the disadvantages of large rigidity and stiffness of the original bamboo fiber, the dyeing is relatively easy, the strength is good, the toughness and wear resistance are high, and the spinnability is excellent, but the environmental protection effect and the health care performance are not as good as the production of the original bamboo fiber recycled bamboo fiber. The methods mainly include solvent spinning and viscose fiber method. Bamboo fiber main characteristics Moisture absorption and permeability: Under the 2000x electron fiber microscope, the cross section of bamboo fiber is deformed and deformed, and it is filled with pores similar to elliptical shape. It is highly hollow and has a strong capillary effect, which can absorb and evaporate moisture in an instant. Among the natural fibers, bamboo fiber has good moisture absorption and moisture permeability and is the first of the five major fibers. Antibacterial and antibacterial: Bamboo fiber has natural antibacterial, antibacterial and bactericidal effects. Because of the special substance “bamboo†in bamboo, it has natural antibacterial, anti-mite, deodorant and insect-proof functions. In cotton and wood fiber products, it can be multiplied, and the bacteria on bamboo fiber products can not only survive for a long time, but also disappear or decrease in a short time. UV resistance: After testing, it was found that for 200~400nm UV, the penetration rate of cotton is 25%, the penetration rate of bamboo fiber is less than 0.6%, and its UV resistance is 41.7 times that of cotton. Ultraviolet rays of this wavelength are the most harmful to the human body. The reflectivity of bamboo fiber fabric to ultraviolet light is lower than that of hemp fabric and cotton fabric, and the bamboo fiber has a stronger absorption effect on ultraviolet light. Green environmental protection: The extensiveness and availability of resources, mainly in the short growth cycle of bamboo, can be completed in 2~3 years, and long-term operation in one planting, bamboo can grow up about 1m overnight, it can grow rapidly and It can be replaced by resources such as cotton and wood for sustainable use. Bamboo fiber can be naturally degraded in the soil, and it has no pollution to the environment after decomposition. It is a natural, green and environmentally friendly textile raw material. Natural health care: Modern medicine believes that the antioxidants in "Bamboo Element" can effectively remove free radicals and ester peroxidates in the human body, and can block the strong carcinogen N-nitrite compound, which can not only significantly improve The body's immunity and biological effects of moisturizing the skin and anti-aging. Deodorization and adsorption: The special ultra-fine pore structure inside the bamboo fiber makes it have strong adsorption capacity, and can absorb harmful substances such as formaldehyde, benzene, toluene and ammonia in the air, and eliminate bad odor. application Bamboo fiber can be purely spun or blended with cotton, wool, hemp and chemical fiber to produce woven fabrics and knitted fabrics of various specifications. The bamboo fiber textiles are cool and breathable in summer and autumn. The winter and spring seasons are both fluffy and comfortable, and can remove excess heat and moisture from the body. The textiles made from it are called “human second skinâ€. Women'S Recycled Slippers,Candy Color Slippers,Flat Sandals For Women,Women Sandals Flip Flops Huaian sunrise shoes Co.,Ltd , https://www.hssindoorslippers.com